https://www.facebook.com/groups/405813783372378/
Catenation is the bonding of atoms of the same element into a series, called a chain.
A chain or a ring shape may be open if its ends are not bonded to each other (an open-chain compound), or closed if they are bonded in a ring (a cyclic compound).
Catenation occurs most readily with carbon, which forms covalent bonds with other carbon atoms to form longer chains and structures


Carbon is most well known for its properties of catenation, with organic chemistry essentially being the study of catenated carbon structures (and known as catenae).
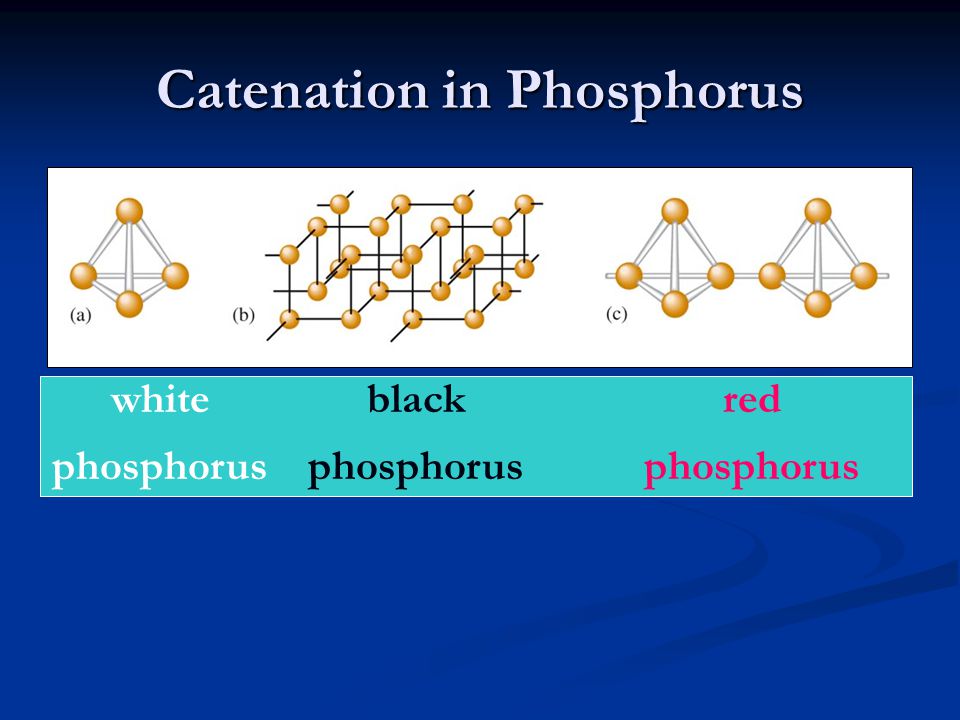
However, carbon is by no means the only element capable of forming such catenae, and several other main-group elements are capable of forming an expansive range of catenae, including silicon, sulphur boron and phosphorus
However, carbon is by no means the only element capable of forming such catenae, and several other main-group elements are capable of forming an expansive range of catenae, including silicon, sulphur boron and phosphorus


No comments:
Post a Comment