Nebivolol:
Join our facebook page for discussions and further good quality learning :
https://www.facebook.com/groups/405813783372378/
Nebivolol is a β1 receptor blocker with nitric oxide-potentiating vasodilatory effect used in treatment of hypertension and also for left ventricular failure.
It is highly cardioselective under certain circumstances.

β1-selectivity
Beta blockers help patients with cardiovascular disease by blocking β receptors, while many of the side-effects of these medications are caused by their blockade of β2 receptors.
For this reason, beta blockers that selectively block β1 adrenergic receptors (termed cardioselective or β1-selective beta blockers) produce fewer adverse effects (for instance, bronchoconstriction) than those drugs that non-selectively block both β1 and β2 receptors.
In a laboratory experiment conducted on biopsied heart tissue, nebivolol proved to be the most β1-selective of the β-blockers tested, being approximately 3.5 times more β1-selective than bisoprolol.
However, the drug's receptor selectivity in humans is more complex and depends on the drug dose and the genetic profile of the patient taking the medication.
The drug is highly cardioselective at 5 mg.In addition, at doses above 10 mg, nebivolol loses its cardioselectivity and blocks both β1 and β2 receptors.
While the recommended starting dose of nebivolol is 5 mg, sufficient control of blood pressure may require doses up to 40 mg).
Furthermore, nebivolol is also not cardioselective when taken by patients with a genetic makeup that makes them "poor metabolizers" of nebivolol (and other drugs) or with CYP2D6 inhibitors.
As many as 1 in 10 whites and even more blacks are poor CYP2D6 metabolizers and therefore might benefit less from nebivolol's cardioselectivity although currently there are no directly comparable studies.
Vasodilator action :
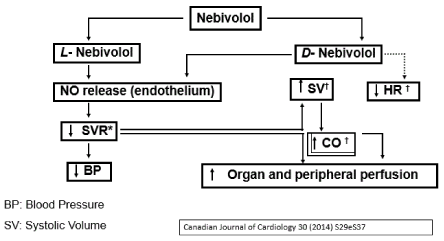
Nebivolol is unique as a beta-blocker.Unlike carvedilol, it has a nitric oxide (NO)-potentiating, vasodilatory effect via stimulation of β3 receptors.Along with labetalol, celiprolol and carvedilol, it is one of four beta blockers to cause dilation of blood vessels in addition to effects on the heart.
Antihypertensive effect :
Nebivolol lowers blood pressure (BP) by reducing peripheral vascular resistance, and significantly increases stroke volume with preservation of cardiac output.
The net hemodynamic effect of nebivolol is the result of a balance between the depressant effects of beta-blockade and an action that maintains cardiac output.
Pharmacology of side-effects :
Several studies have suggested that nebivolol has reduced typical beta-blocker-related side effects, such as fatigue, clinical depression, bradycardia, or impotence.However, according to the FDA.

Contraindications:
Nebivolol is contraindicated in patients with severe bradycardia, heart block greater than first degree, cardiogenic shock, decompensated cardiac failure, sick sinus syndrome (unless a permanent pacemaker is in place), severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh > B) and in patients who are hypersensitive to any component of the product.
Nebivolol is also associated with warnings regarding abrupt cessation of therapy, cardiac failure, angina and acute myocardial infarction, bronchospastic diseases, anesthesia and major surgery, diabetes and hypoglycemia, thyrotoxicosis, peripheral vascular disease, non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers use, as well as precautions regarding use with CYP2D6 inhibitors, impaired renal and hepatic function, and anaphylactic reactions.
Contraindications Summay :
Severe bradycardia
Heart block greater than first degree
Patients with cardiogenic shock
Decompensated cardiac failure
Sick sinus syndrome (unless a permanent pacemaker is in place)
Patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B)
Patients who are hypersensitive to any component of this product.
Adverse drug reactions
Headache
Paresthesia
Dizziness
History

No comments:
Post a Comment