Mechanism of Salicylate / Aspirin Toxicity:
Acute Aspirin Toxicity stimulates the central respiratory centre and leads to respiratory alkalosis by causing tachypnea.
Aspirin causes an anion gap metabolic acidosis by 3 main mechanisms:
1. Salicylate toxicity causes uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation thereby causing an increase in rate of oxygen consumption in peripheral tissues .This uncoupling is also the cause of hyperpyrexia seen in aspirin toxicity.
2.Salicylate toxicity causes inhibition of enzymes involved in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism leading to accumulation of organic acids such as pyruvate,lactic acid and acetoacetic acid.
3.Salicylates impair renal function causing accumulation of inorganic acids such as sulfuric acid and phosphoric acids.

Biochemical presentation:
Salicylate toxicity can present with a mixed respiratory alkalosis and metabolic acidosis which is characterized by a near normal pH , a decrease in PaCO2 and a concurrent decrease in HCO3-.
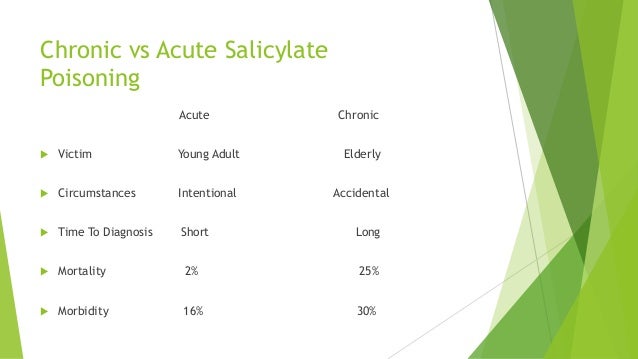
Clinical Features include :
Tinnitus
Fever
Tachypneasis.
Vomiting
Respiratory Alkalosis
Anion Gap Metabolic Acid
No comments:
Post a Comment