Join our facebook page for discussions and further good quality learning :
https://www.facebook.com/groups/405813783372378/
Enalapril,is a medication that belongs to the angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor (ACEi) family of medications. used to treat high blood pressure, diabetic kidney disease, and heart failure.
For heart failure it is generally used with a diuretic such as furosemide.

Mechanism of action
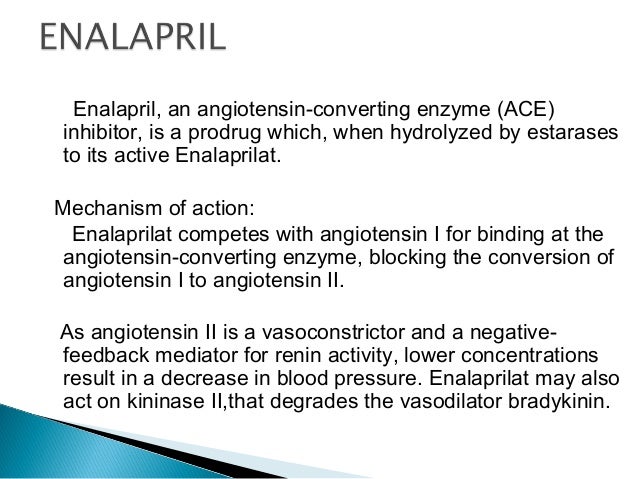
Normally, angiotensin I is converted to angiotensin II by an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). Angiotensin II constricts blood vessels, increasing blood pressure.
Enalaprilat, the active metabolite of enalapril, inhibits ACE. Inhibition of ACE decreases levels of angiotensin II leading to less vasoconstriction and decreased blood pressure.
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetic data of enalapril:
Onset of action: about 1 hour
Peak effect: 4–6 hours
Duration: 12–24 hours
Absorption: ~60%
Metabolism: prodrug, undergoes biotransformation to enalaprilat.
Route of administration :
It is given by mouth or injection into a vein.
Onset of effects are typically within an hour when taken by mouth and last for up to day.
Medical uses
Enalapril is used to treat hypertension, symptomatic heart failure, and asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction.
It has been proven to protect the function of the kidneys in hypertension, heart failure, and diabetes, and may be used in the absence of hypertension for its kidney protective effects.
It is widely used in chronic kidney failure.
Furthermore, enalapril is an emerging treatment for psychogenic polydipsia.
A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial showed that when used for this purpose, enalapril led to decreased water consumption (determined by urine output and osmality) in 60% of patients.

.
Side effects
Common side effects include headache, tiredness, lightheadedness with standing, and cough.
Serious side effects include angioedema and low blood pressure.
Use during pregnancy is believed to result in harm to the baby.
The most common side effects of enalapril include increased serum creatinine (20%), dizziness (2–8%), low blood pressure (1–7%), syncope (2%), and dry cough (1–2%).
The most serious common adverse event is angioedema (swelling) (0.68%) which often affects the face and lips, endangering the patient’s airway.
Angioedema can occur at any point during treatment with enalapril, but is most common after the first few doses.
.
Enalaprilat was developed partly to overcome these limitations of captopril. The sulfhydryl moiety was replaced by a carboxylate moiety, but additional modifications were required in its structure-based design to achieve a potency similar to captopril. Enalaprilat, however, had a problem of its own in that it had poor oral availability. This was overcome by the researchers at Merck by the esterification of enalaprilat with ethanol to produce enalapril.