Aerodynamics
Aerodynamics is the study of the motion of air, particularly its interaction with a solid object, such as an airplane wing.
Aerodynamics is a sub-field of fluid dynamics and gas dynamics, and many aspects of aerodynamics theory are common to these fields.
The term aerodynamics is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, the difference being that "gas dynamics" applies to the study of the motion of all gases, and is not limited to air.
Aircraft
A machine that can fly, held aloft in the air, is called an aircraft.
Airplanes and helicopters are two types of aircraft.
Some kinds of aircraft, primarily helicopters, use rotors or spinning blades to fly, while the lift of other aircraft comes from jet engines or the shape of the aircraft's wing.
Still other aircraft, including hot air balloons, use buoyancy ,generally a gas that's lighter than airfor lift and flight.
Balloons were actually the first vehicles referred to as aircraft, along with airships. The word was adapted from nautical terminology.
Airplane
Airplane is an aircraft that has a fixed wing and is powered by propellers or jets.
An airplane is a flying vehicle that has fixed wings and engines or propellers that thrust it forward through the air.
It's most common when you travel long distances to take an airplane.

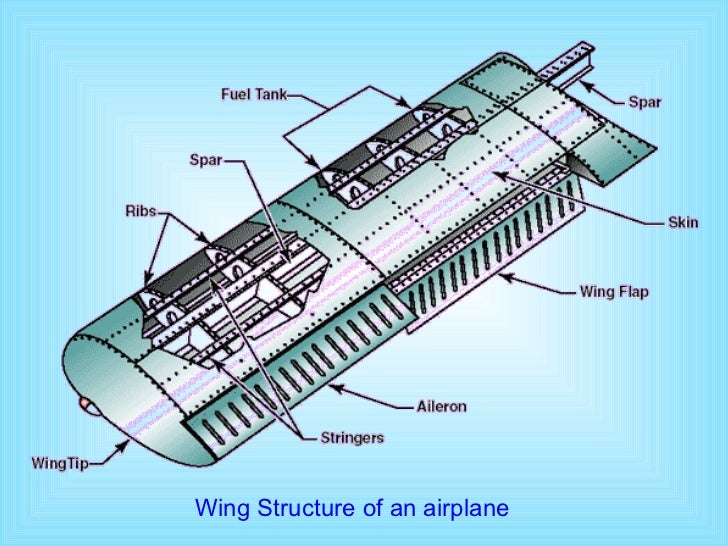
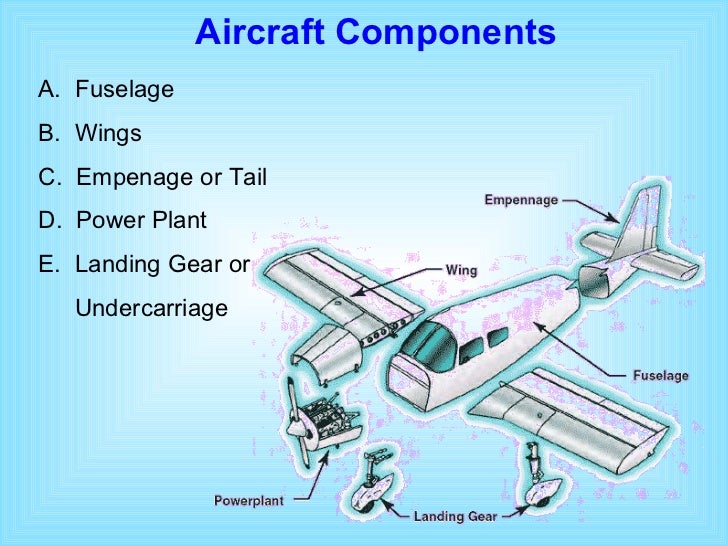
/airplane-nasa-56a058985f9b58eba4affc95.jpg)









/airplane-nasa-56a058985f9b58eba4affc95.jpg)