Aspirin Ingestion
Ethylene Glycol Poisoning
Methyl Alcohol Ingestion
Uremic Acidosis
Lactic Acidosis


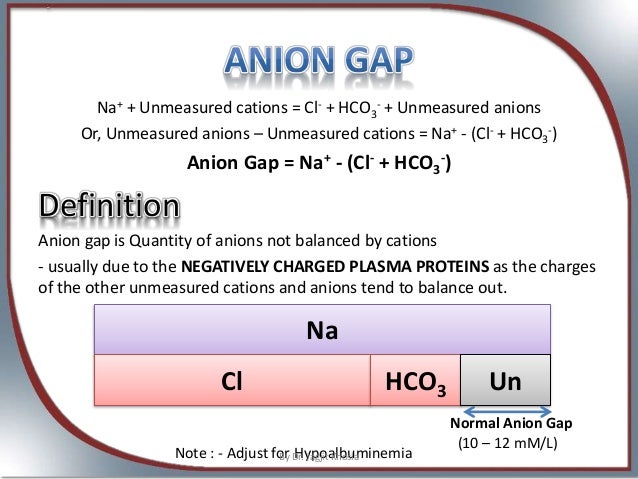
Normal Anion Gap is 6 - 12
pH less than 7.35 is indicative of Metabolic Acidosis.
In patients with markedly elevated anion gap and if frank uremia is not present,the osmolar gap should be calculated to assess for ethanol,methanol or ethylene glycol intoxication.

The serum Osmolality is calculated by using the following formula :
Serum Osmolality = 2 (Na + Glu / 18 + BUN /2.8 )
The Osmolar gap is calculated by the following formula :
Osmolar Gap = Observed Osmolarity - Calclated Osmolarity.
Osmolar Gap metabolic acidosis is seen in :
Acute Methanol
Ethanol or
Ethylene glycol.
Ethylene Glycol Poisoning
This occurs following antifreeze ingestion.
It is characterized by presence of rectangular envelope shaped calcium oxalate crystals in the urine.
Serious sequelae of this poisoning include :
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Heart failure
Renal failure
Aspirin / salicylate toxicity causes :
Mixed Anion gap metabolic acidosis and respiratory alkalosis with no osmolar gap.
Methyl Alcohol poisoning :
This causes visual changes ( snowfield vision ) and acute pancreatitis.
It doesnot cause renal failure or urine crystals.
Uremia / Renal failure :
It can cause anion gap metabolic acidosis due to failure to excrete acids.

Lactic Acidosis
can result from numerous causes including poor delivery of oxygen to the tissues and poor oxygen utilization by the tissues.
The result is an anion gap metabolic acidosis.
No comments:
Post a Comment