Human blood pH is maintained between 7.35 - 7.45.
This is done by various mechanisms the most significant being regulation of CO2, carbonate and hydrogen atoms by the lungs and the kidneys.


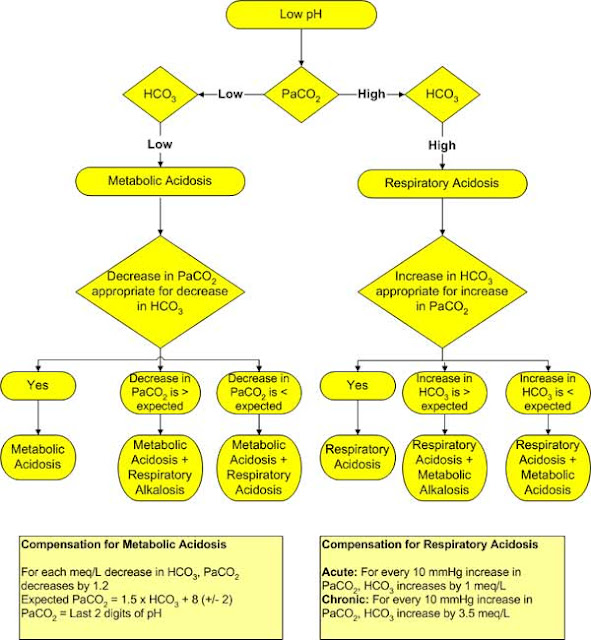
A pH of more than 7.45 is considered alkalosis and a pH of less than 7.35 is considered acidosis.

The pCO2 and HCO3- values can then be used to differentiate between a respiratory or a metabolic cause of acid base disturbance.
The normal HCO3- is 24 meq/l and the normal PCO2 is 40 mmHg.

Any deviation from these normal values is indicative of an acid base disorder.
Metabolic acid base disorders are due to a primary change in concentration of HCO3 while respiratory acid base disorders are due to a primary change in PCO2.
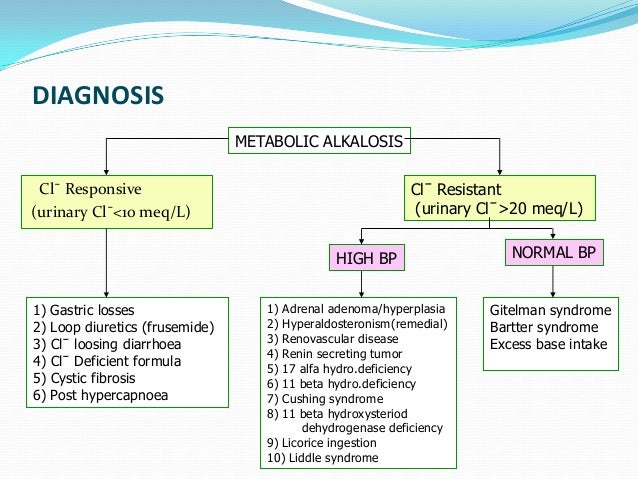
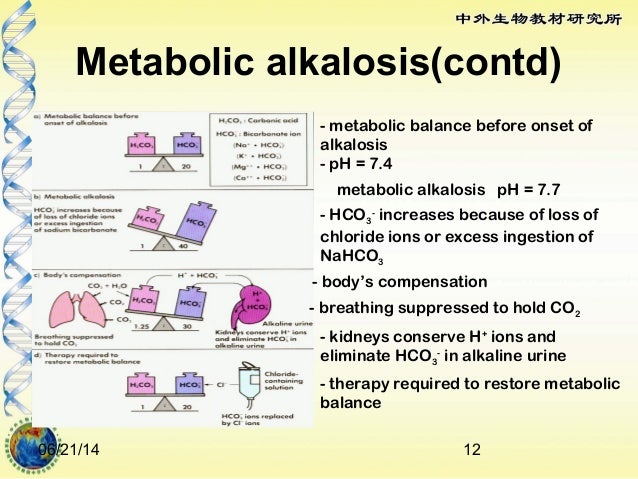
Main causes of Metabolic Alkalosis includes :
Exogenous administration of an alkali.
Removal of acidic gastric secretions due to vomiting or NG tube aspiration.
Renal Hydrogen ion loss due to mineralocorticoid excess
Contraction Alkalosis.

No comments:
Post a Comment